The healthcare industry is saturated with problems, and patients and medical staff are stuck in the middle. With so much change in the world with technology, why is the American healthcare system still lagging behind?
Here is a list of 20 of the most embarrassing healthcare statistics, feel free to share this with your colleagues.
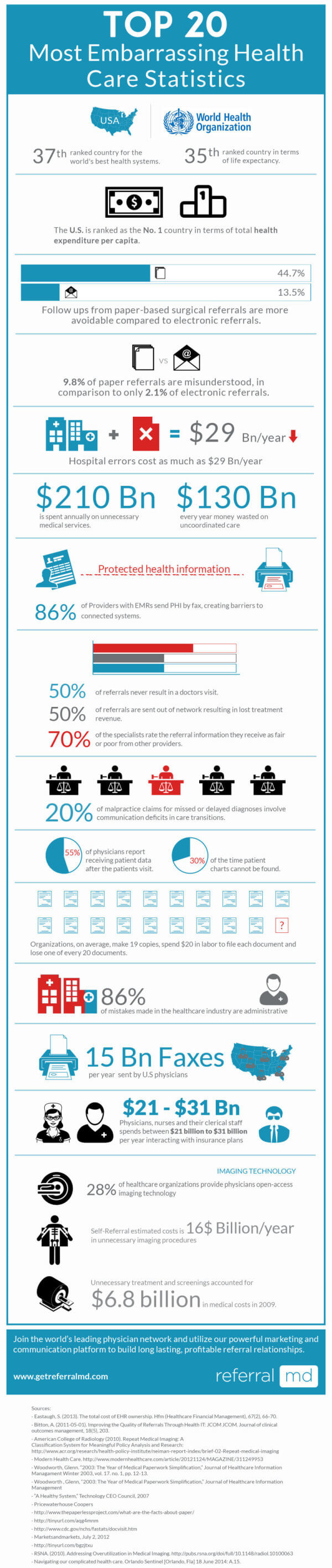
Top 20 Most Embarrassing Health Care Statistics:
- The U.S. is ranked as the 37th country for the world’s best health systems and is 35th in regards to life expectancy, as reported by the World Health Organization.
- The U.S. is ranked as the No. 1 country in terms of total health expenditure per capita.
- 44.7% of paper-based surgical referrals are avoidable, compared with only 13.5% of electronic referrals.
- 9.8% of paper referrals are misunderstood, in comparison to only 2.1% of electronic referrals.
- Hospital errors cost as much as $29 Bn/year
- $210 Billion is spent annually on unnecessary medical services, and $130 Billion is wasted on uncoordinated care
- 86% of Providers with EMR send PHI by fax. Can’t communicate with other platforms.
- 50% of referrals never result in a doctor’s visit
- 70% of the specialists rate the referral information they receive as fair or poor from other providers.
- 20% of malpractice claims for missed or delayed diagnoses involve communication deficits in care transitions.
- 55% of physicians report receiving patient data after the patient’s visit.
- Organizations, on average, make 19 copies, spend $20 in labor to file each document and lose one of every 20 documents.
- 86% of mistakes made in the healthcare industry are administrative
- Patient charts cannot be found on 30% of visits
- 15 billion faxes are still sent by US physicians every year
- Physicians, nurses and their clerical staff spends between $21 billion to $31 billion per year interacting with insurance plans
- Only 28% of healthcare organizations provide physicians open-access imaging technology
- Self-Referral estimated costs is $16 Billion/year in unnecessary imaging procedures
- Up to 50% of referrals are sent out of network resulting in lost treatment revenue. (Referral Leakage)
- A study from October 2011, in the Archives of Internal Medicine, estimated that unnecessary treatment and screenings accounted for $6.8 billion in medical costs in 2009. This does not include the costs of the additional testing or procedures that may have been caused by a false positive initial result.