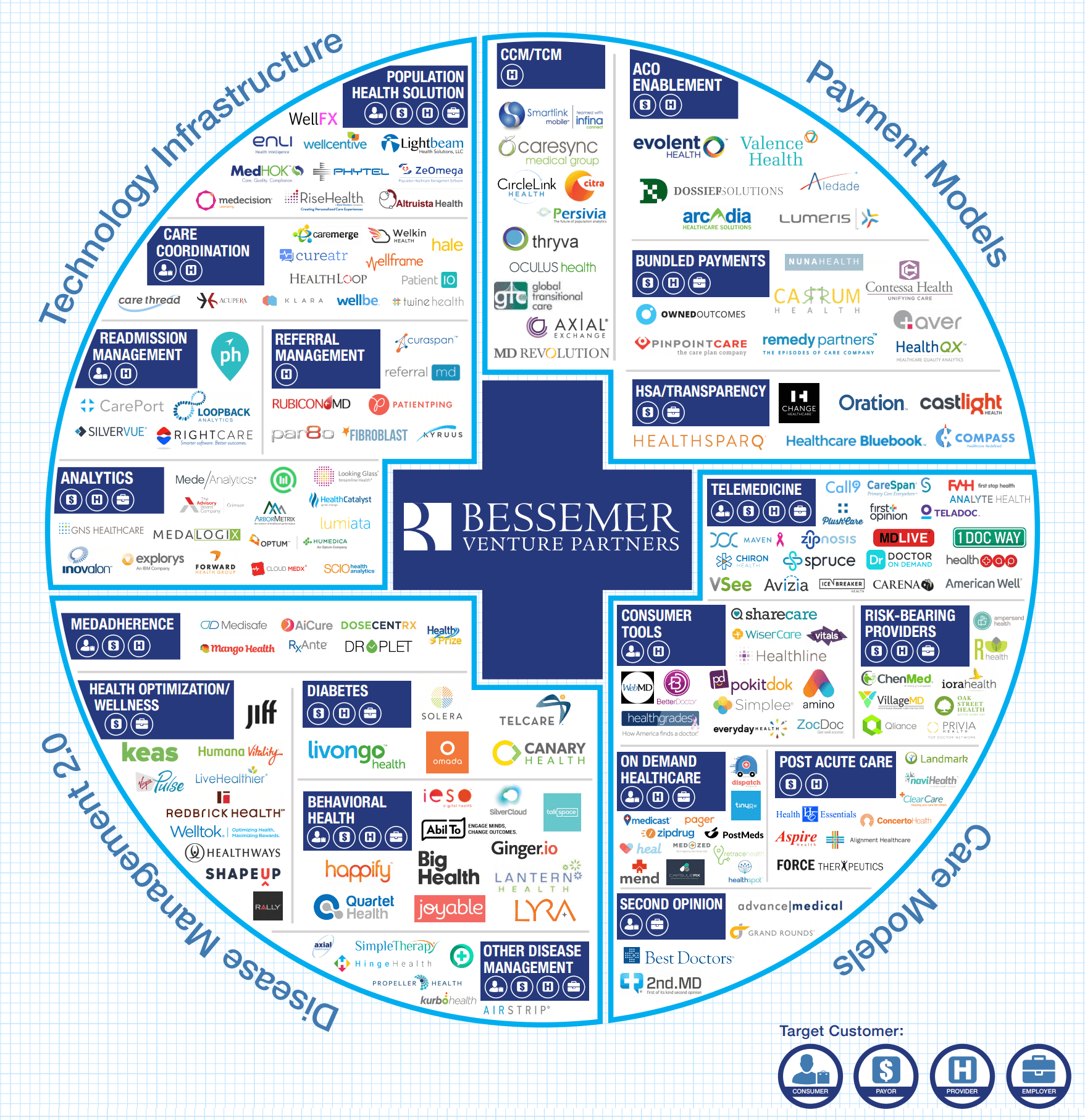
Check out the healthcare trends we tracked in 2021:
Healthcare Technology Trends from 2021
See what we were thinking about in 2020:
Healthcare Technology Prediction from 2020
The ReferralMD Annual Healthcare Technology Report of 2016.
2016 is shaping up to be one of the biggest years for healthcare technology ever, with innovations in health technology devices, software, and changes in how healthcare is administered, both from a care and financial perspective. The North American health IT and technology market is expected to reach $104 billion by 2020 at a CAGR of 13.5% during the forecast period of 2015 to 2020, according to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets. A majority of this growth is attributed to the growing adoption of various healthcare IT solutions by healthcare providers in order to meet the heightened regulatory requirements for patient care and safety, increasing need to curtail the soaring healthcare costs, and the growing need to improve the quality of healthcare while maintaining the operational efficiency of healthcare organizations.
Update: Read the latest technology review for 2017
Top 17 Healthcare Technology Advances of 2017
Link to Techcrunch Article:
So what does that mean to you? The healthcare professional: Doctor, Dentist, Referral Coordinator, Nurse, PA, Front/Back office, Billing, Scheduling, Risk Manager, Marketing, and (…). It means, (/crosses fingers) that your lives and your patients will be getting better over the course of the next few years with some amazing technology. With healthcare accounting for almost 1/5th of our GDP, we need to start making serious investments in improvements that can help all of our country and the world’s people together.
Here are some of the top healthcare technologies from 2016 looking forward…
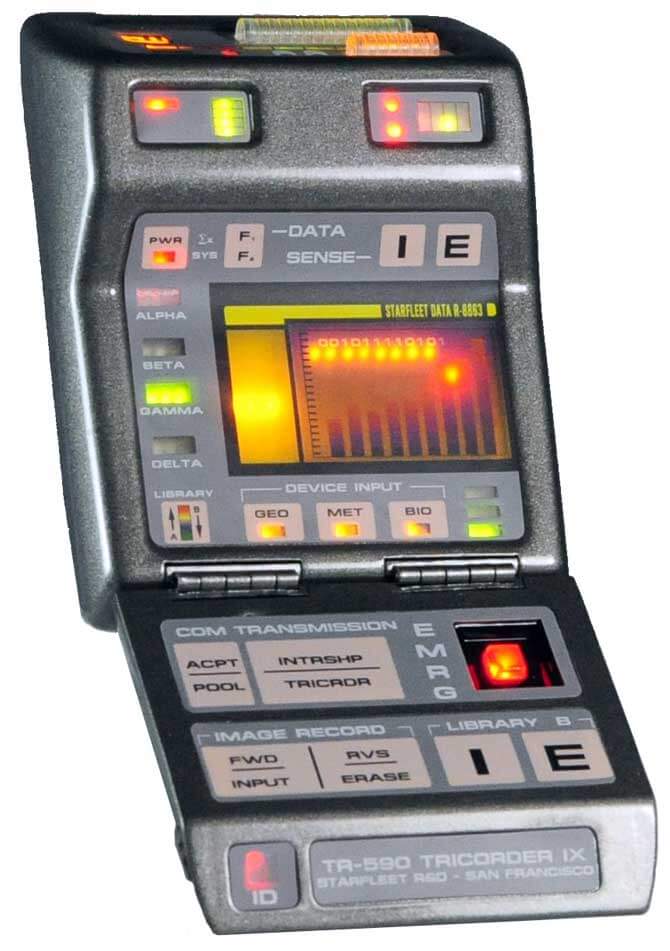
1. The Star Trek Style Tricorder
To start off, Yes I am a Star Trek Nerd, loved almost every series, especially TNG (The Next Generation), and no not because I shave my head like Patrick Stewart.

Star Trek: The Next Generation
Patrick Stewart as Captain Jean-Luc Picard
Star Trek has always inspired millions of people, including myself to reach beyond what we thought was possible and achieve the impossible. And futuristic medical devices are no different. Qualcomm has a contest, called XPrize, that was just extended till 2017 for 7 final teams developing the almighty Tricorder featured in the picture below from the popular Star Trek series. The winner receives $10 million to bring the device to reality.
In the fictional Star Trek universe, a tricorder is a multifunction hand-held device used for sensor scanning, data analysis, and recording data. Three primary variants of the tricorder appear in Star Trek, issued by the fictional organization Starfleet. The standard tricorder is a general-purpose device used primarily to scout unfamiliar areas, make a detailed examination of living things, and record and review technical data. The medical tricorder is used by doctors to help diagnose diseases and collect bodily information about a patient.
2. Interoperability between Health Systems
Interoperability solutions for exchanging patient information across care settings is one particular technological development that will shape the future of healthcare organizations.  Value-based care and health information exchanges are an increasingly important part of the overall healthcare landscape, and the ability for all providers – from general practitioners and specialists to post-acute care organizations, etc. – will only grow as a critical component of care delivery in the future. These types of solutions have only started being developed in the past few years by companies such as referralMD, which are changing how healthcare companies communicate by including post-acute care providers in critical interoperability workflows, as these providers are expected to be a big part of health care cost containment.
Value-based care and health information exchanges are an increasingly important part of the overall healthcare landscape, and the ability for all providers – from general practitioners and specialists to post-acute care organizations, etc. – will only grow as a critical component of care delivery in the future. These types of solutions have only started being developed in the past few years by companies such as referralMD, which are changing how healthcare companies communicate by including post-acute care providers in critical interoperability workflows, as these providers are expected to be a big part of health care cost containment.
![]()
By including post-acute care in interoperability strategies, healthcare organizations can ensure that critical patient information across all care settings will be connected, providing a more detailed patient picture for more specific treatment plans and improved patient care. The statistics are damning, hospitals lose $75+ million per year per 100 affiliated physicians due to referral leakage, a burden that can be reduced by proper referral network management that companies such as referralMD can help monitor. Hospitals are just starting to get make changes in their budgets to include programs that can truly help patients receive better care, and save their staff’s time in the process. Not only are hospitals affected but so are small-to-mid-sized practices, with many having to juggle 100’s of specialty offices with different workflow requirements, without an electronic way to exchange information, the process breaks down, information is not accurate, and time is wasted.
3. Robotic Nurse Assistant
I have many friends that are nurses that are injured every year from having to move or lift patients in bed or after an emergency from a fall. The problem is very common and many times there is not someone around that is strong enough to lift a patient immediately after one of these occurrences. There are many variations from a full robot such as RIBA (Robot for Interactive Body Assistance) developed by RIKEN and Tokai Rubber Industries and assisted hardware such as HAL (Hybrid Assistive Limb) robot suits delivered by Cyberdyne.

RIBA is the first robot that can lift up or set down a real human from or to a bed or wheelchair. RIBA does this using its very strong human-like arms and a novel tactile guidance method using high-accuracy tactile sensors. RIBA was developed by integrating RIKEN’s control, sensor, and information processing and TRI’s material and structural design technologies.

A company by the name of HAL is a robotics device that allows a care worker to lift a patient with more stability and strength and helps prevent injuries to our nurses.
4. Artificial Retinas
The United States typically defines someone as legally blind when the person’s central vision has degraded to 20/200, or the person has lost peripheral vision so that he sees less than 20 degrees outside of central vision. Normal vision is 20/20, and people can usually see up to 90 degrees with their peripheral vision. An estimated 1.1 million people in the United States are considered legally blind. This has led companies like Nano-Retina to develop a sophisticated and elegant solution intended to restore the sight of people who lost their vision due to retinal degenerative diseases. The miniature Nano Retina device, the NR600 Implant, replaces the functionality of the damaged photoreceptor cells and creates the electrical stimulation required to activate the remaining healthy retinal cells. NR600 consists of two components; a miniature implantable chip and a set of eyeglasses worn by the patient.

It’s very interesting technology for those that are always sitting in front of the computer like myself, hopefully, it will not be needed by me, but it’s great that companies are advancing for those that suffer this debilitating illness.
5. Advances in Prosthetics
War is in our DNA, and with conflict, there are injuries to our Military including loss of limbs and traumatic brain injury. DARPA is looking to change that by enabling wounded service members with amputations to neurally control state-of-the-art prosthetic limbs. The goal is to assist them in returning to active duty and improving their quality of life. Program developments may impact the broad community of patients with medical amputations, spinal cord injuries, and neurological diseases. The challenges lie with creating an interface that is directly compatible with our own nervous system and making the connection fast enough to interpret our movement intent without latency. I have been following Les’s story (an amputee) for a while and featured it in a 2015 version of this article, see video below and wanted to showcase it again as organizations such as Johns Hopkins are making great strides in the movement to help the world live and easier life.
5. Remote Patient Monitoring
Monitoring programs can collect a wide range of health data from the point of care, such as vital signs, weight, blood pressure, blood sugar, blood oxygen levels, heart rate, and electrocardiograms. This data is then transmitted to health professionals in facilities such as monitoring centers in primary care settings, hospitals and intensive care units, skilled nursing facilities, and centralized off-site case management programs. Health professionals monitor these patients remotely and act on the information received as part of the treatment plan. Monitoring programs are tools to help achieve the “triple aim” of health care, by improving patient outcomes and access to care, and making health care systems more cost-effective. For example:
- In a 2014 study, a six-month feasibility study was conducted on eight patients with a history of Acute Exacerbation of CODP (AECOPD). Each patient was given a mobile app to record major symptoms, such as dyspnoea, sputum color, and sputum volume; minor symptoms such as cough and wheezing; and vital signs. During the trial, the rate of hospital admissions was significantly lower and there were fewer ED presentations and GP visits compared to a six-month matched period in the preceding year. Such results showed “the potential of home monitoring for analyzing respiratory symptoms for early intervention AECOPD.”
- Similar to our previous Star Trek device, a company in Israel, Tyto Care, has developed a portal device that helps monitor all sorts of health parameters to let doctors diagnose patients remotely. Allowing your doctor to perform their job with accurate metrics about you or your child’s illness without having to resort to an in-person visit. The Tyto device is currently going through the FDA clearance process, hopefully, offering people the option of staying at home rather than visiting the clinic.
“We are coming together at a pivotal time in the mobile healthcare industry. As health reform demands more focus on delivering quality outcomes and reducing costs, providers are turning to technology like remote monitoring to diagnose and treat more patients in ways that use time, money and human resources efficiently and effectively. Our shared vision is to become a worldwide leading remote monitoring company,” said Jon Otterstatter, President and Chief Global Strategy Officer of Preventice Inc.
6. Anti-Aging Drugs
The dream, or the nightmare, depending on how you take it, is living forever, or at least in the foreseeable future to 120+ years old. 2016 will be the year of a new anti-aging drug test that will enter trials that could see diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s consigned to distant memory.
Scientists now believe that it is possible to actually stop people from growing old as quickly and help them live in good health well into their 110s and 120s.
Although it might seem like science fiction, researchers have already proven that the diabetes drug metformin extends the life of animals, and the Food and Drug Administration in the US has now given the go-ahead for a trial to see if the same effects can be replicated in humans.
“This would be the most important medical intervention in the modern era, an ability to slow ageing”Dr Jay Olshansky, University of Illinois Chicago
If successful it will mean that a person in their 70s would be as biologically healthy as a 50-year-old. It could usher in a new era of ‘geroscience’ where doctors would no longer fight individual conditions like cancer, diabetes, and dementia, but instead treat the underlying mechanism – aging.
The new clinical trial called Targeting Aging with Metformin, or TAME, is scheduled to begin in the US next winter. Scientists from a range of institutions are currently raising funds and recruiting 3,000 70 to 80-year-olds who have or are at risk of, cancer, heart disease, and dementia. They are hoping to show that drug slows the aging process and stops disease.

Outlining the new study on the National Geographic documentary Breakthrough: The Age of Ageing, Dr. Jay Olshansky, of the University of Illinois Chicago, said: “If we can slow aging in humans, even by just a little bit it would be monumental. People could be older and feel young.
“Enough advancements in aging science have been made to lead us to believe it’s plausible, it’s possible, it’s been done for other species and there is every reason to believe it could be done in us.
“This would be the most important medical intervention in the modern era, an ability to slow aging.”
7. Tooth Regeneration
Hey Kids, here is some candy! All kidding aside, this could be an amazing advancement if the technology holds true in the coming years.
Colorful fish found in Africa may hold the secret to growing lost teeth. In a collaborative study between the Georgia Institute of Technology and King’s College London, researchers looked at the cichlid fishes of Lake Malawi in Africa, who lose teeth just to have a new one slide into place. Their study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, identifies the genes responsible for growing new teeth and may lead to the secret to “tooth regeneration” in humans.
“The exciting aspect of this research for understanding human tooth development and regeneration is being able to identify genes and genetic pathways that naturally direct continuous tooth and taste bud development in fish, and study these in mammals,” said the study’s co-author Paul Sharpe, a research professor from King’s College, in a press release. “The more we understand the basic biology of natural processes, the more we can utilize this for developing the next generation of clinical therapeutics: in this case how to generate biological replacement teeth.”
Another study from a Harvard team successfully used low-powered lasers to activate stem cells and stimulate the growth of teeth in rats and human dental tissue in a lab. The results were published today in the journal Science Translational Medicine. Stem cells are no ordinary cells. They have the extraordinary ability to multiply and transform into many different types of cells in the body. They repair tissues by dividing continually either as a new stem cell or as a cell with a more specialized job, such as a red blood cell, a skin cell, or a muscle cell.
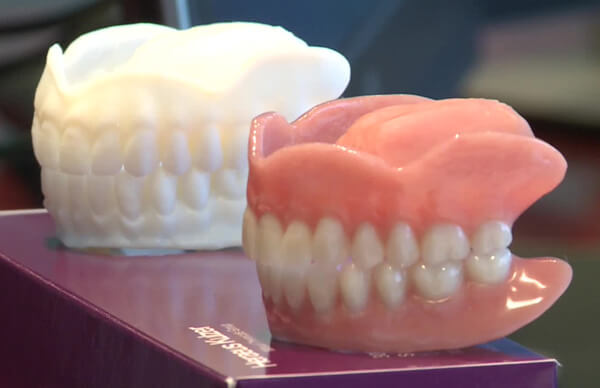 Dentures and dental implants may soon become a thing of the past. Stem cell research is making it possible to regrow your missing teeth!
Dentures and dental implants may soon become a thing of the past. Stem cell research is making it possible to regrow your missing teeth!
This is a much-needed medical advancement, especially considering that by age 74—26% of adults have lost all of their permanent teeth.
8. Lightbulbs that Disinfect and Kill Bacteria
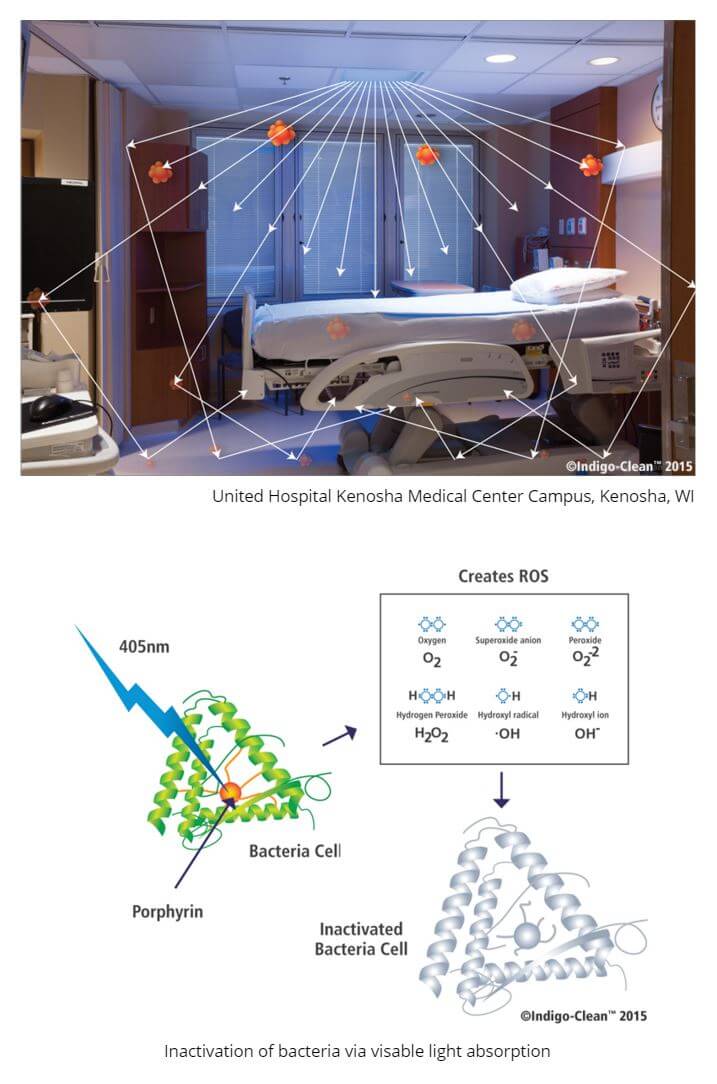 Hospitals are known to be potentially dangerous place with lot’s of people with different elements and diseases. One company, Indigo-Clean has developed a technology using visible light that continuously disinfect the environment and bolsters your current infection prevention efforts.
Hospitals are known to be potentially dangerous place with lot’s of people with different elements and diseases. One company, Indigo-Clean has developed a technology using visible light that continuously disinfect the environment and bolsters your current infection prevention efforts.
How it works
- The 405nm emitted from Indigo-Clean reflects off of walls and surfaces, penetrating harmful micro-organisms
- The light targets naturally occurring molecules called porphyrins that exist inside bacteria. The light is absorbed and the excited molecules produce Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) inside the cell
- 405nm creates a chemical reaction inside the cell, similar to the effects of bleach
- The Reactive Oxygen Species inactivates the bacteria, preventing it from re-populating the space
9. Electronic Underwear Preventing Bed Sores
Having elderly grandparents that have died from complications due to bedsores is extremely unfortunate, as much of these issues could be prevented. When patients stay motionless for days, weeks, or months they develop painful open wounds due to lack of circulation and compressed skin. These wearable devices can help!

And believe it or not, bedsores can be deadly<. Roughly 60,000 people die from bed sores and resulting infections every year, draining $12 billion from the U.S. medical industry.
Developed by Canadian researcher Sean Dukelow of Project SMART, the electric underpants—deliver a small electrical charge every ten minutes. The effect is the same as if the patient was moving on their own—it activates muscles and increases circulation in that area, and effectively eliminates bed sores, thereby saving lives.
10. Long Lasting Batteries for Medical Devices and Wearables
The need for power is evident in today’s world, for our houses, cars, and medical devices such as pacemaker batteries that typically need to be replaced with an expensive surgery. With the need for power-hungry devices comes innovation in the form of new technologies that will help provide the world with longer lasting, faster charging batteries.
-
- Aluminum-Ion Batteries: Chemistry Professor Hongjie Dai from Stanford University and his team say their aluminum-ion battery prototype can fully charge a phone in one minute and maintain its strength through thousands of recharge cycles — over seven times as many cycles as current phone batteries. But fast charging times aren’t the only advantage this new prototype has over the standard lithium-ion battery found in most of our devices. Perhaps the battery’s most impressive quality is its flexibility, meaning it could work with any future devices that are curved or use bendable screens.
- Micro Supercapacitors:Rice University researchers who pioneered the development of laser-induced graphene have configured their discovery into flexible, solid-state micro super capacitors that rival the best available for energy storage and delivery. Rice’s micro super capacitors charge 50 times faster than batteries, discharge more slowly than traditional capacitors and match commercial super capacitors for both the amount of energy stored and power delivered.
- Foam Batteries: The future of batteries is 3D. Prieto is the first company to crack this with its battery that uses a copper foam substrate. This means these batteries will not only be safer, thanks to no flammable electrolyte, but they will also offer longer life, faster charging, five times higher density, be cheaper to make and be smaller than current offerings.
- Skin Power: Researches from the National University of Singapore have created a replacement for batteries all together would be an electrode used to harvest the current caused by friction on the skin and clothes. The result is enough power, from a finger tap on skin, to power 12 LED bulbs. The future could mean there are no need for batteries in wearables or smart clothes. So how does it work? An electrode is used to harvest the current, so a 50nm-thick gold film is used. The gold film sits below a silicone rubber layer composed of thousands of tiny pillars that help create more surface area for skin contact, which creates more friction. Since the skin is a one of the triboelectric layers it means the device can be small. Scientists have already shown off a wearable powered by the device. Next gadgets to use it? Hopefully everything.
11. Health Informatics
More than half of US hospitals use some type of electronic records system, but only 6% meet all the federal mandates, according to a recent study out of the University of Michigan. According to researchers at the University of Chicago, 50% of health care dollars are wasted on inefficient record-keeping processes. Electronic records have been shown to save large hospitals anywhere between $37 and $59 million. It streamlines the medical care process and lowers malpractice claims, and increases coordination between providers. Improvements still need to be made communicating patients between facilities as noted from referralMD, (Provider-to-provider communication software) where roughly 50% of all patients do not attend appointments, driving costs upwards, and lowering patient outcomes dramatically.

Practitioners and medical researchers can look forward to technologies that enable them to apply data analysis to develop new insights into finding cures for difficult diseases. Healthcare CIOs and other IT leaders can expect to be called upon to manage all the new data and devices that will be transforming healthcare as we know it.
According to Sam Volchenboum, director of the Center for Research Informatics at the University of Chicago,
“2016 will be the year of liberated health data.” In his upbeat estimation, the coming year will bring patients more-informed treatments, faster rates of innovation, and new ways of “mashing up” healthcare data, leading to greater insights into hard-to-crack diseases like cancer.
We have already heard news that Meaningful Use may not even survive past 2017 according to Andy Slavitt, acting CMS Administrator. Specifically, according to a Family Practice Newsreport, Slavitt said,
“The meaningful use program as it has existed will now be effectively over and replaced with something better.” He continued, per the report, “We have to get the hearts and minds of physicians back. I think we’ve lost them.” Slavitt noted that the focus will move away from rewarding providers for the use of technology and towards the outcomes they achieve with their patients.
What does this mean to everyone? Your guess is as good as mine, but my opinion is that the current systems are not working, and do not model after today’s workflow requirements for physicians and their staff to work efficiently. Most EMR systems were haphazardly put together to capitalize on the gold rush of free money offered by the government and scaled prematurely. No normal startup receives that much free cash that quickly, usually the market squashes companies that put out a bad product, but not the case with today’s environment.
12 – 15
Watch a short video that shows some amazing technologies:
12. Plug a Gun Shot with Tiny Sponge
13. See veins under the skin in real-time
14. Gel that stops bleeding in seconds
15. Cholesterol removing machine
Conclusion: Movement to Embrace Technology by Health Systems
The movement has begun with most health systems such as Ascension Health, Dignity Health, Stanford and others investing into startups, albeit very slowly. Many health systems are just now beginning to build their own innovation centers, but have not yet built the framework on how to judge their performance and key metrics.
With the advent of virtual reality, Hackathons and schools such as Hack Reactor and General Assembly, we are seeing many more people join the digital revolution. The future is bright, start investing in startups, you will be rewarded with amazing technology and possibly financial success.
Here’s to a great year!