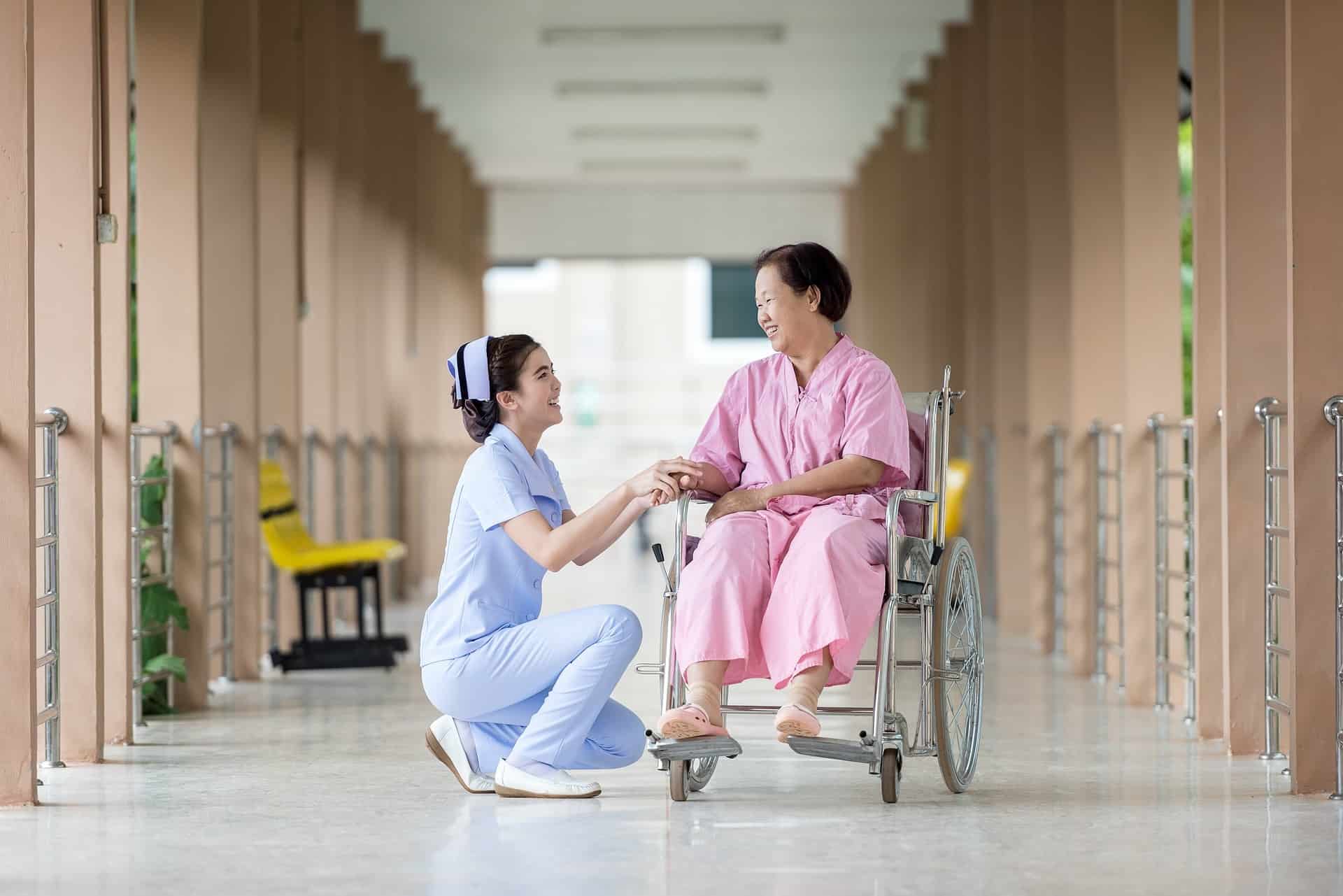
Why should you be concerned with increasing your understanding of health and healthcare services? As a major portion of our population ages, we struggle to maintain wellness and quality of life for the elderly. But success for a patient takes a whole team of people working together — from patients and their families to caregivers, clinicians, and other healthcare providers. All of these people involved can work together better and more effectively if they all share a solid understanding of the healthcare services needed for the patient.
Unfortunately, our society doesn’t do a great job of educating patients and even some caregivers, and the responsibility often lies on the shoulders of healthcare professionals. But helping your patients to understand their health and the healthcare services you’re offering or recommending to them will improve the likelihood of success, improving the patient’s trust in you and your practice.
Image Source: Pixabay
When we improve health literacy, we also improve the overall health of our communities by enabling people to understand their health better and maintain wellness. This can also be achieved by helping people ask their providers more relevant questions and preparing them with the knowledge needed to point friends and family to pertinent medical services.
But creating a broader understanding of health and healthcare services for your patients isn’t easy. You’ve spent all your time learning how to care for patients and then building a patient-centric practice; we don’t want to add more work to your plate. So this article will show you how to help your patients understand what you’re doing for them and why you’re doing it through training personnel, knowing procedures and how to explain them to patients, and sharing patient data. Let’s get started.
Personnel

Image Source; Pixabay
A part of understanding your health and healthcare services is understanding the roles and duties of the healthcare professionals you encounter. From the front desk to your medical assistants, practitioners and their personnel should all be proficient communicators. They should be equipped with the necessary knowledge to explain their role and duties to patients.
Try introducing each professional and their role as soon as they meet with a patient or caregiver. For example, medical assistants do a lot for patients. But it would be helpful to explain what that person’s role is and how it will be applied to the specific patient’s needs. To make things easy, you could have informational guides that explain what a medical assistant is or what a lab tech does with their test samples. Patients feel more comfortable knowing exactly who is involved in their healthcare and how this person is helping them.
It’s also important to train and educate your employees. Educating your employees about your practice will enable them to provide better customer service to your patients through more information and guidance. Here are some tips to help health professionals communicate to improve patient understanding:
- Avoid using medical jargon
- Show interest in questions
- Take time explaining forms
- Confirm understanding with techniques such as teach-back and visual aids
- Provide educational packages with videos and multimedia programs
- Develop programs for low-literacy populations specifically
Effective communication between healthcare professionals and patients is important in explaining roles and helping patients better understand recommended procedures.
Procedures
Image Source: Pixabay
Nobody wants to go under the knife without knowing what to expect. It’s always important to explain why a procedure is needed and what exactly is happening. It’s also important that patients, their families, and caregivers understand their care needs post-procedure.
For example, an influx of well-meaning parents armed with misinformation regarding vaccines has led to recent outbreaks of diseases like measles that were previously considered wiped out. Physicians and other healthcare staff can help combat this by researching vaccines and educating their patients.
Likewise, it’s a good idea to inform patients of your sanitation and cleaning procedures. Research shows that a patient’s perception of a hospital’s cleanliness can impact their experience and overall care. Patients worry about the risk of hospital-acquired infections and what the hospital and staff are doing to prevent contamination and infection. Both cleanrooms and hospitals should follow the same contamination prevention procedures, and so should your practice. Cleanliness matters to patients and their families, so take time to explain what you’re doing to prevent contamination in your practice.
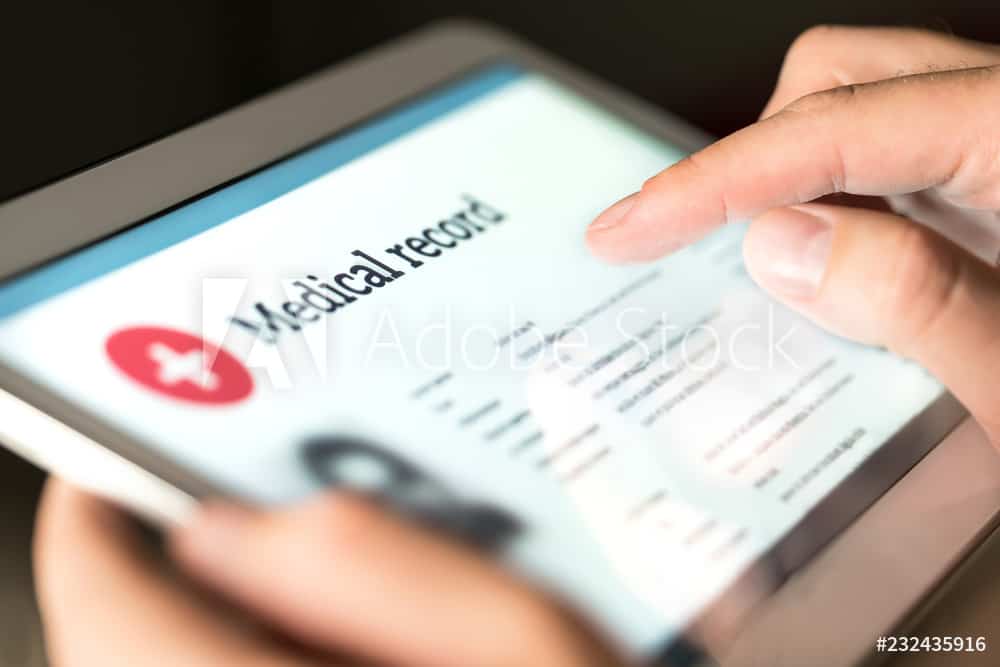
Patient Data

Image Source: Pixabay
Another aspect of healthcare confusion for patients regards their medical health records and data. What is it? Where is it stored? Who has access to it? How can I get it? And how do I know it’s safe? These are just some of the questions people are wondering, and it’s for a good reason. The healthcare industry in the U.S. is highly vulnerable to data breaches. According to healthcare experts with Norwich University, 9 million patient health records were compromised in breaches in 164 incidents in 2014, and researchers noted a 600 percent increase in hacking attacks on hospitals. Hackers can acquire names, birth dates, social security numbers, healthcare ID numbers, home addresses, email addresses, employment information, and even income data.
This poses not only a risk to your patients but your practice and reputation as well. Norwich University also reports the average cost to health organizations of a data breach is $2.1 million per incident and can include:
- Class-action lawsuits
- Disruptions in your business operations
- Identity-theft repair
- Investigation and remediation
- Lost business
- Notification to patients
- Regulatory Fines
But there are actions you can take to prevent a data breach, and you should be informing your patients of what you’re doing to protect them. First, you should be aware of what cyberattacks are and where you might be vulnerable to an attack. Hiring personnel with the technical expertise to identify and prevent data breaches or allocating a percentage of your budget to digital security can also help protect your practice and your patients tremendously.
While nothing guarantees your patient data is safe from hackers, here is a list of tips you can use to increase protection and prevent easy access:
- Regularly assess your IT systems to identify risks and vulnerabilities.
- Understand the different causes of data breaches.
- Provide training and development opportunities for your staff.
- Ensure employees understand HIPAA and other laws.
- Cultivate a culture of security, knowledge, and awareness.
- Use encryption to protect patient medical data stored electronically.
- Use level access limitations, so patient data is only accessible to specific personnel.
- Maintain ownership of your patient’s data instead of using cloud service providers.
- Secure, reliable legal support before a breach happens.
- Regularly back up your data in case it needs to be recovered after a breach.
- Establish policies for employees that use their own devices.
- Regularly update hospital devices and minimize unnecessary apps.
- Use multifactor authentication.
Never wait for an incident to happen before you think about cybersecurity. It’s best to plan for the worst and hope for the best.
Access to Medical Records

Image Source: Pixabay
When patients have access to their medical records, it’s easier to understand their healthcare services and what they’re paying for. But it’s often challenging to access your patient medical records.
Even though patient data is often available online, research shows that patients and caregivers still have trouble accessing the information they need, even though their own physician’s online patient portal. Patients who need more detailed data have to use a request process that is often confusing and slow.
But even health systems medical records managers struggle with the arduous process of acquiring medical records. Improving the process overall is the only solution. Application program interfaces (APIs) and mobile apps could help improve the process by providing secure access to health information. But for now, it’s a good idea to create a user-friendly medical records request process.
Insurance and Financing

Image Source: Pixabay
Like understanding one’s medical records, patients need to understand their insurance and who pays for their healthcare services. This gets tricky as the current U.S. health insurance system is confusing at best. Unfortunately, there’s not much you can do to help a patient with their insurance other than ensuring your personnel is as informed as possible. Much of this responsibility falls on the individual’s employer-provided benefits representative if they have one. Or through their research into their healthcare plans.
You can, however, provide patients with information to help them pay for their services or procedures through financial assistance programs. Explain to your patients that an elective surgery gives them the time they need to find help paying for their procedure, but emergency surgery could put them in a tough spot. You don’t want to have to worry about your medical bills during and immediately after receiving treatment for a broken bone, hernia repair, or gallbladder removal, for example, especially if you are unable to work after the surgery.
Whether your patients have insurance or not, they will be grateful to receive literature or brochures on programs such as medical loans, settlement programs, unemployment benefits, charity help, or Medicare from their doctor. If you want to go above and beyond, you can collect insurance information for the in-network programs you participate in.
Assess Health Literacy

Image Source: Wikimedia
Health literacy is how well an individual can obtain, process, and understand health information and services needed. It is largely dependent on things like culture, existing knowledge of health topics, and communication skills. When individuals understand their health (i.e., they are health literate), they can better communicate their needs with healthcare professionals, better able to understand and fill out complex forms and navigate the healthcare system. They are better able to engage in their self-care and disease management.
In practice, how do you know your patients understand you and their health needs? Here are some tips for assessing health literacy and improving understanding:
The first and most important tip is to ensure you’re communicating effectively. Use communication methods like metaphors, analogies, music, and stories when plain speaking and writing aren’t working. But the most important aspect of communicating yourself clearly and to people of all different ages, cultures, and backgrounds is to speak with simple and concise language. Use plain language — words, terms, and concepts people already know — to explain health and healthcare services.
Once you’ve honed in your communication style and have used simple and concise language when communicating with patients, try to confirm understanding. Even in your best attempts to communicate clearly, sometimes understanding just doesn’t come through. When you’re struggling to convey information, try the teach-back method. If you’re not already familiar with the teach-back method, it’s simple. Just ask your patient or their caregiver to repeat back to you the information you just gave them, in their own words. Here are some best practice tips to ensure the teach-back method is effective:
- Use language that is plain, simple, clear, and concise.
- Teach in small chunks and ask for repeat-back multiple times.
- If the individual still isn’t understanding the information you’re trying to convey, try a different approach to explaining it, like the previously mentioned metaphors, analogies, and stories.
- Use pamphlets or handouts to help support your explanation.
- Encourage all questions.
We’ve mentioned that brochures, pamphlets, metaphors, analogies, music, and stories can all help support your communications with patients by improving understanding. Getting creative with your materials can help clarify complicated health topics as well. Try building or obtaining tangible materials like pictures, illustrations, drawings, molds, visuals, or even puppets to help public understanding.
Finally, it’s important to remember that it’s not only essential to encourage questions, but as a healthcare provider, you must also clarify and ask questions. Start by asking if the patient has any questions and then clarify to ensure your understanding of their question. Using the teach-back method and asking clarifying questions will help identify knowledge gaps and any misunderstandings so you can clear them up with a further explanation.
Creating a broader understanding of health and healthcare services benefits individuals in need and leads to healthier families and communities. Healthcare professionals can help improve understanding and literacy by finding effective ways of communicating by working together to explain procedures better and share data. What are you doing in your practice to help patients better understand their care? Let us know what you’ve done in a comment below.












