Summary:
Around this time of year, everyone writes about predictions and trends. The article provides an eagle-eyed view of the evolving landscape of the healthcare industry. We will look at major healthcare technology trends from 2018 and the upcoming challenges and opportunities to keep in consideration for 2019. With every passing year, the advances in technology impact different sectors and such is the case for the healthcare industry as well. Healthcare is marked with different growth patterns and trends which vary within its different sub-domains. The patterns include multivariate growth of some domains contradicted with inconsistent stagnation in others.
1. Diagnostics will have a Patient-Centric Approach
With the radical change in the set of expectations that a consumer has today, the need for consumerism as a trend to be incorporated in the business model is increasing to an appreciable extent. Front-end changes are not expected to suffice the need of consumerism when it comes to the diagnostic aspect of patient care. Thus, the diagnostic entities are embracing the superior methods for staying ahead in the value-driven system.
- Major pharma players are also investing in the consumer genetics field for the development of novel pharmaceutical products.
- In this regard, GlaxoSmithKline entered into a four-year collaboration with 23andMe; one of the leading players in the genetic testing market; for drug discovery through human genetics.
Clinical decision-making is expected to advance in order to provide simple, standardized, effective, and efficient patient experience across the care spectrum focusing on prevention, illness, and chronic care wellness, by the virtue of a comprehensive strategy such as consumer genomics and precision medicine.
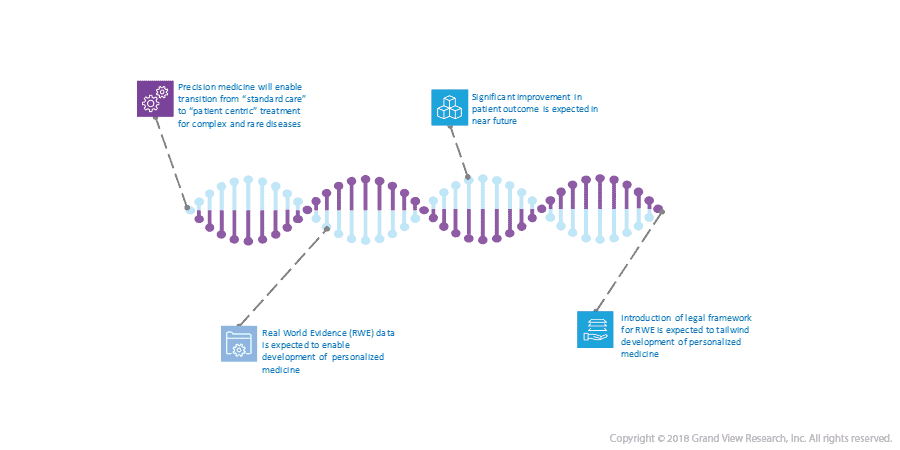
A) Precision Medicine: Transforming The Way Complex Diseases Are Analyzed
Treatment of complex and rare diseases is witnessing a shift in trend from “patient engagement” to “patient-centricity”. This patient-centric approach deals with creating a fundamentally new value proposition for individual patients thus increasing therapeutic success rates, treatment adherence, and patient compliance. Thus, 2018 witnessed an increase in the adoption of strategic changes for the treatment of complex and rare diseases.
In previous decades, treatments based on the clinical symptoms most commonly observed in patients were pivotal to standard medical care. However, precision medicine is designed to rationalize various medical attributes of patients such as genetic make-up, prior treatment history, behavioral preference, and environmental conditions, thus developing a customer-centric treatment for complex diseases.
Moreover, the personalized medicine approach is expected to provide a higher patient outcome for complex diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s which are caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- The Real World Evidence (RWE) data is enabling researchers to develop more efficacious personalized treatments.
- Data collected from a patient registry, interventional clinical trials, Electronic Medical Records (EMR), and medical claim data is further used to develop personalized medicines for cancer and other rare diseases.
B) 2017 Momentum Snowballing In 2018 For Precision Medicine
Currently, a substantial number of precision medicine initiatives are underway which include Million Veterans initiative for military veterans, UK’s ‘100,000 Genomes Project, and Oncology Precision Network for Cancer. Increased support for various precision medicine initiatives and strong potential to avoid revenue loss due to a patent cliff is expected to change the clinical pipeline development strategy of the participants in order to align with the market trend.
A record number of 16 personalized medicines were approved in 2017 by FDA, which contributed significantly to building the momentum for this trend in 2018. These personalized medicines are approved for the treatment of several conditions which include orphan diseases e.g. Mucopolysaccharidosis type VII (Sly syndrome) and CLN2 Batten disease, infectious diseases such as Hepatitis C, and cancer therapies for myeloid leukemia, breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma.
2. Gene Editing Technologies will Advance
Gene editing technologies in diagnostic platforms are in the making to change the face of disease detection, bio-sensing, and diagnostics in 2019 and beyond. Moreover, it can also prove equally viable in the field of agriculture, biomanufacturing, and forensics.
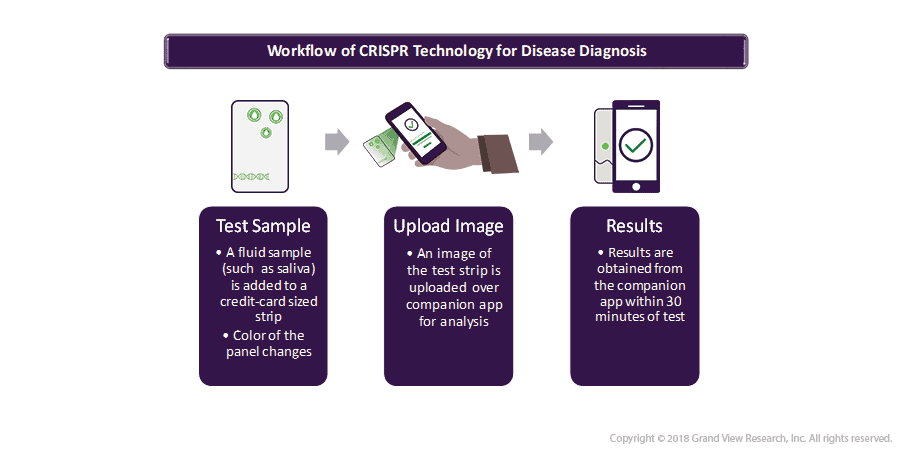
CRISPR can transform the utility of complex laboratory-based disease diagnostic tests into home diagnostic kits that are as easy to operate similarly to that of a pregnancy detection kit. Thus, it can serve as an easy point-of-care solution for the diagnosis of complex disorders.
- In mid-2018, Mammoth Biosciences launched the first of its kind CRISPR-based diagnostic platform for the detection of diseases.
- Similar developments are expected in the along the year 2019 as the platform is easily programmable to locate a wide range of DNA- or RNA- based targets. Thus, CRISPR based diagnostics is expected to aggrandize with the discovery of more and more biomarkers in the future.
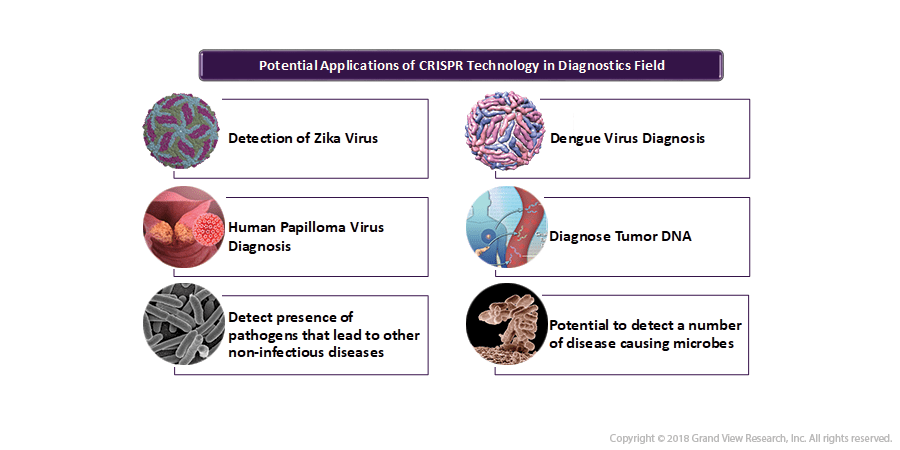
CRISPR applications span almost every field that is based on the biological system which includes food, laboratory, and medical applications. Considering the scope of such a wide array of applications of CRISPR/Cas9 technology, across multiple industries, this genome editing method is projected to stimulate substantial economic activity for the launch of novel agro and industrial products.
However, CRISPR still needs to conquer the controversy around the idea of ‘man-made’ alterations to the human genome, apart from the ongoing patent litigations and infringement suits. Moreover, the safety concerns raised by Novartis and Karolinska Institute over CRISPR in 2018, for weakening the ability to fight a tumor within the patient needs to be dealt with.
3. Exosomes will be seen as Potential Targeted Therapy
Exosomes, the endosome derived extracellular vesicles of 30–120 nm size are recognized as the mediators of cell-to-cell communication and are considered to be up-and-coming as well as promising candidates for the suppression of cancer growth & metastasis. Moreover, exosomes are utilized as nano-carriers for immunotherapy of inflammatory diseases as these possess the ability to transfer proteins and nucleic acids from one cell to another.
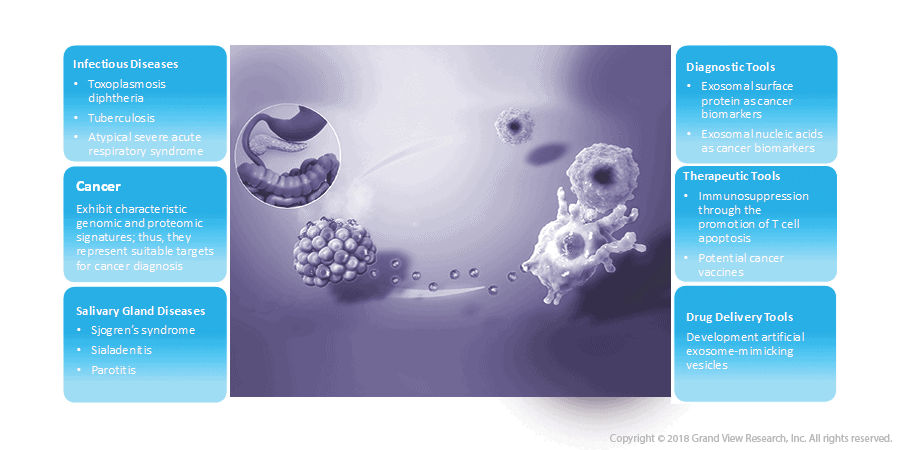
- Additionally, exosome-mediated transport plays a vital role in diverse mechanisms such as epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) signaling, angiogenesis & metastasis, and hypoxia as exosomes exhibit anti or protumorigenic properties.
- Owing to the anti or protumorigenic properties, exosomes can promote or suppress cancer growth via variation of intercellular communication inside the tumor microenvironment.
- Potential applications of exosomes are still being studied for solving drug delivery problems for indications such as RNA therapies, viral gene therapy, and small molecules as well as in CRISPR gene-editing tools.
- Moreover, recent studies also reveal that exosomes, when derived from stem cells, could be utilized as regenerative medicine.
- Further research related to exosome identification and secretion might allow the development of novel diagnostic, therapeutic, and preventive approaches as well as aid in targeting specific cancer cells.
However, certain risks associated with the usage is expected to reduce the unproven usage of these therapies, which has been increasing in the past years. With the explosion of stem cell exosome research in translational medicine, the proven way of clinically approved trials would serve as a green flag for exosome derived products.
4. Coherent Omnichannel Approaches will Drive Pharmaceuticals
The current pharmaceutical model is neither economically sustainable nor operationally capable to meet the demand of the evolving marketplace. The incapacity to deliver solutions in terms of both quality and quantity in the face of rising global disease burden calls for an immediate change in the pharmaceutical operations. Gone is the time when companies were rewarded for selling the highest volume or developing the most innovative product on the shelf; the modern times clamor for value addition to health services, additional benefits, and better reimbursement policies.
- Business communication strategies are likely to be focused on consumer needs and expectations. The omnichannel approaches aim to provide top-class customer experience and promote maximum customer interaction.
- An omnichannel approach, being a brand-new concept with no reference point, requires key leaders to take smart risks and the will to experiment with business strategies.
- Technological advancements necessitate smart skill sets, a coherent integration with the IT backbone, and a flexible model to tailor-fit the forthcoming customer needs.
- Since market variables are subject to change on a regional level, global experiences are likely to scale up this new strategy into more favorable outcomes.
A) The Road Ahead
- It goes without saying that the pharmaceutical industry faced intense competition in 2018. The stand-off competition among players makes it crucial for them to capitalize on every opportunity in the coming years.
- Supply chains must be customized according to the product type and target patient base. Supply chains can be applied for market segmentation for achieving the methodical flow of services and commodities.
- Value-added healthcare services based on customer needs is the key to success.
- Pharmaceutical market operations must transform to improve operational production and economic sustainability.
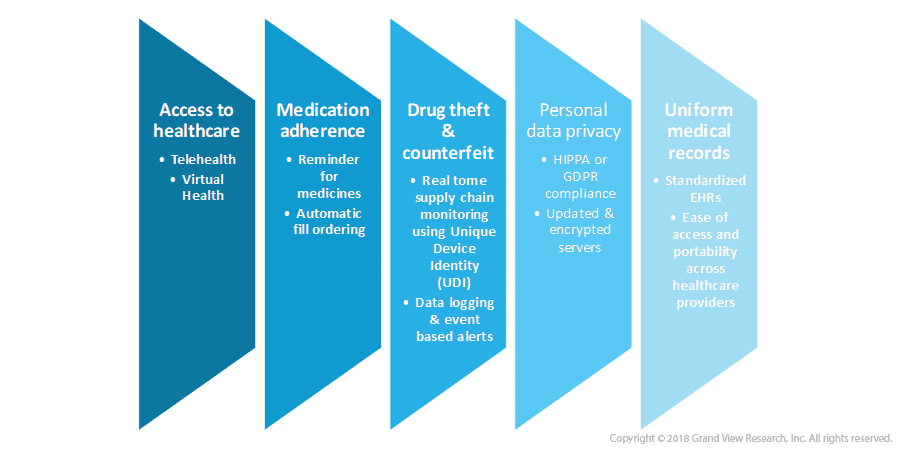
5. Digital Challenges will Manage Healthcare
Cloud technology is a part of everyday life, from backing up photos to saving documents, we get cloud storage with a click of a button. However, as it sounds the healthcare system is the most challenging system to transform, owing to the huge number of legacy systems, highly sensitive data, and inconsistent data monitoring legislation.
There is an increasing pressure on healthcare providers to lower the costs and improve patient care (do more with less). The challenges in the digital transformation of the healthcare industry can be visualized considering the process of version control when it comes to managing millions of non-uniform electronic patient records, integrating with social and healthcare information, personal data privacy, drug theft, and counterfeiting and developing infrastructure to connect countless trusts, hospitals, surgeries, and clinics.
Following challenges can be furbished up with the help of cloud computing technology in the years to come:
A) Use Of Real World Evidence While Launching A Drug Into A Market
The data collection and generation apart from clinical trials is nowadays vital to various pharmaceutical manufacturers.
- Life science tool companies are employing Real World Evidence (RWE) programs for data acquisition from post-marketing activities. The data obtained from RWE can extemporize the entire drug life-cycle and can improve the innovation speed and financial outcomes of drug developers.
- Cloud technology facilitates easy incorporation and use of vast datasets, provide analytical tools, including AI capabilities to efficiently analyze data and provide insights, remotely. This adoption of cloud technology is expected to gain impetus in the coming years owing to its added functionalities.
- However, the pharmaceutical industry must be ready to handle the impact of digitization. Protecting personal data and investments must be at the top of the priority list. Companies must enlist clear data regulation policies to avoid any fraud.
6. 5G Mobile Technology and Implications For Healthcare
Healthcare and fast communication can soon join hands and grow together with the anticipated advent of 5G in healthcare. Though the adoption of 5G enabled devices is expected to be average, this transition from 4G to 5G will certainly open new cloud applications in healthcare.
However, healthcare organizations cannot enforce a cloud culture shift without any assistance and hence may need to outsource some of their IT needs to expert providers, thus increasing the demand for healthcare IT in the years to come. Therefore, it can be said that the future of the “healthcare system lies within the clouds”.
7. Is Artificial Intelligence Radiology’s Superpower?
Artificial intelligence is set to transform the modus operandi of radiology. Medical imaging accounts for nearly 90% of the healthcare data with hospitals storing millions of digital images on a routine basis. Converting such an enormous data in a usable format pronounces the need for AI, in order to tackle the ‘data flood’.
Several healthcare IT biggies, such as GE Healthcare, Philips Healthcare, IBM, Siemens Healthineers, are developing their proprietary AI solutions as integrated offerings with their Healthcare IT franchise, and many others are forming strategic partnerships with vendors in order to harness the development, integration and distribution expertise.
Furthermore, by 2023, even hospitals are anticipated to invest nearly USD 2 billion annually in AI for diagnostic medical imaging as it has proved to improve the patient outcomes and hospital’s Return of Investments (ROI).
- Also to add, AI is giving a tough competition to radiologists and is constantly ‘learning and training’ to outsmart them. For example, a new AI model is capable enough to detect radiograph abnormalities with respect to a wrist and finger radiograph better than radiologists.
- Tech giants such as Microsoft and Google do not want to lose out on the AI bandwagon. Microsoft is exploring the use of AI for detection of early warning signs of a particular disease whereas Google published an article on an AI model that determines the likelihood of patients’ death based on nearly 50 million data pieces.
- Google also announced a new method by which AI can train on patients’ medical records without compromising on data safety & confidentiality. Considering the rapid advances in AI, Geoffery Hinton, a renowned AI researcher, suggested that radiologist training by medical schools should be put to rest.
- Taking a cue from the rising penetration, a tech company in Quebec developed an AI system which reduced the wait times in doctors’ offices by scouring nearly 1.2 million appointments for predicting the actual time a doctor will the patient. This system is estimated to help patients save nearly 6.5 million hours per year in Quebec.
8. Digital Imaging and Pay-Per-Use Rental Scheme
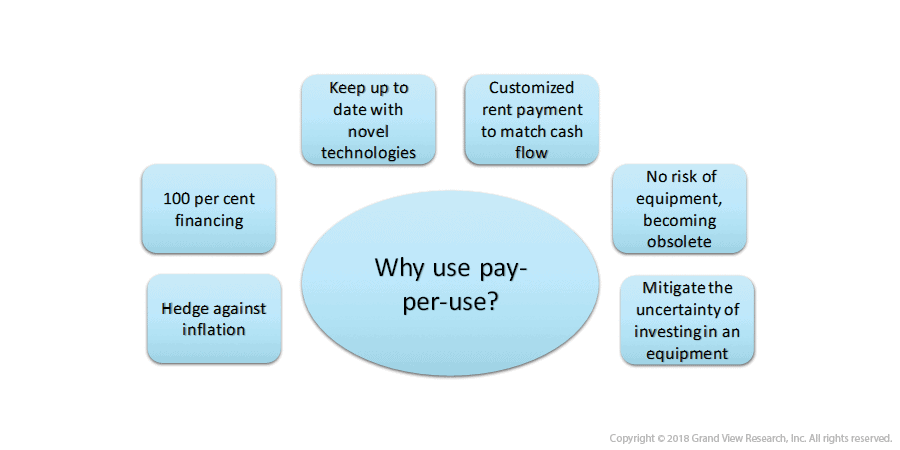
- Rental services offer a solution to the ever-confusing question: ‘buy or lease?’ Rental services require short-term arrangement as compared to leasing and are much cost-effective than buying as these enable immediate accessibility, flexible terms allowing extension options, and little capital outlay.
- In an attempt to empower their clients in making the best suitable decision, certain vendors like Siemens are offering both rental and purchase options to their clients. Furthermore, GE healthcare assists its customers with their financial analysis to derive an appropriate decision.
9. Was 2018 the Year of Product Recalls?
Medical device manufacturers are constantly involved in outsmarting their competitors by rushing to gain the first-mover advantage with their latest innovative products. The fast-paced technological advancements have created a fear of rapid product obsolescence and thus inducing market entities to hastily launch the product into the market. This heightens the risk of the introduction of a potentially hazardous medical device into the market.
The main concern with the rise in product recalls is the increase in the number of Class I recalls. Class I recalls are those devices which are liable to cause serious adverse health consequences or death. The steady increase in Class I recalls in the past three years is becoming a major concern for the industry.
A) Software Bugs Behind Product Recalls
Software issues were the leading cause of the recalls in 2018, accounting for nearly 78 recalls in the quarter, followed by mislabeling, quality, and out of specifications issues. These were the most common problems.
The increasing complexity of the medical devices has increased the risk of software issues as it is becoming increasingly difficult for the imaging leaders to strike the right balance between innovative software and cyber vulnerabilities and identify all the potential failure modes.
The increasing inter-connectivity offered by the latest technologies makes it imperative to understand how the various device and software components work and interact together for curtailment of the probability of a device recall.
Furthermore, medical imaging leaders should become more vigilant and undertake extensive pre and post-marketing testing for efficient management of cyber and software vulnerabilities.
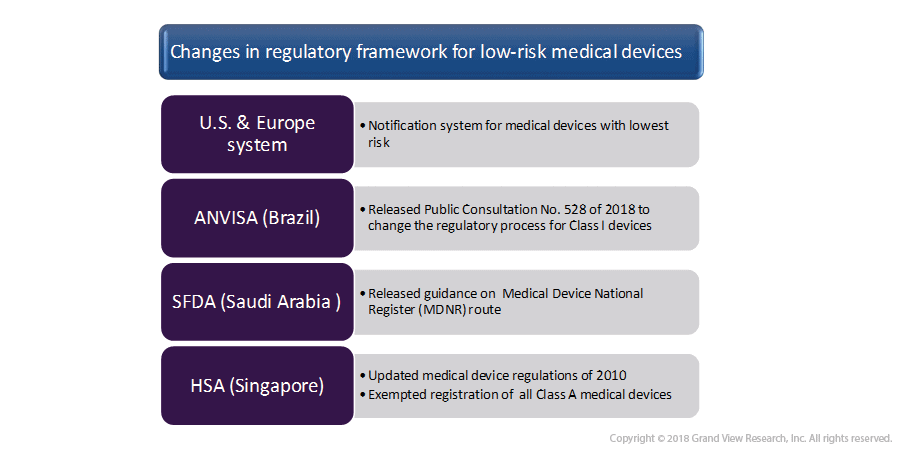
B) Device Tracking And Traceability Was On The Rise In 2018
The year 2018 also observed advancements in the field of medical devices to enhance device traceability and tracking, and simplification of regulatory procedures for low-risk medical devices. The year witnessed an emphasis on regulatory and digital initiatives; such as global naming convention; to assist data collection on devices that are supplied in the market.
Progress has been made to advance the Global Medical Device Nomenclature (GMDN) system so that it is adopted globally. Regulatory bodies have worked to launch device traceability systems that require device identification methods, UDI, and nomenclature. Moreover, development was observed in the adoption of GMDN, and UDI Codes.
C) Simplification Of The Regulatory Process
Regulatory bodies simplified the device approval process for low-risk medical devices. These are given in the figure below:
10. Will Blockchain Make A Difference Addressing Healthcare Challenges?
With the advent of blockchain technology, the storage of medicine-related data has become more secure, thereby increasing its adoption in the healthcare field. The technology finds its applications in a wide range of medical services.
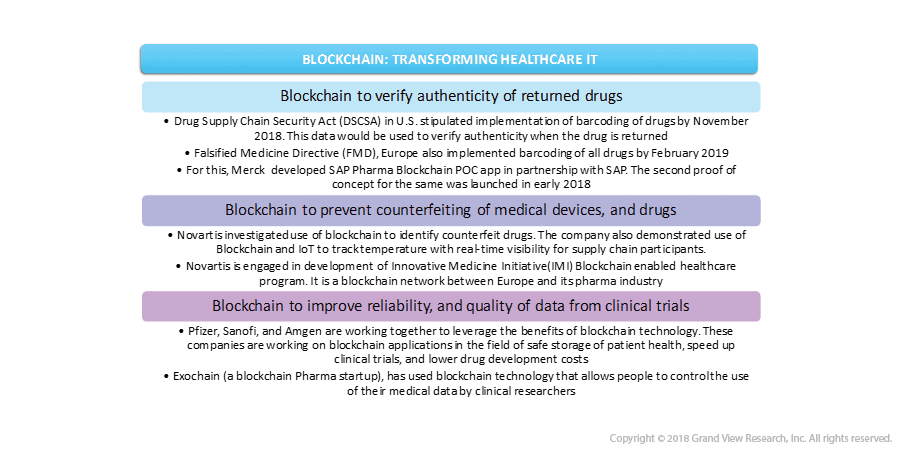
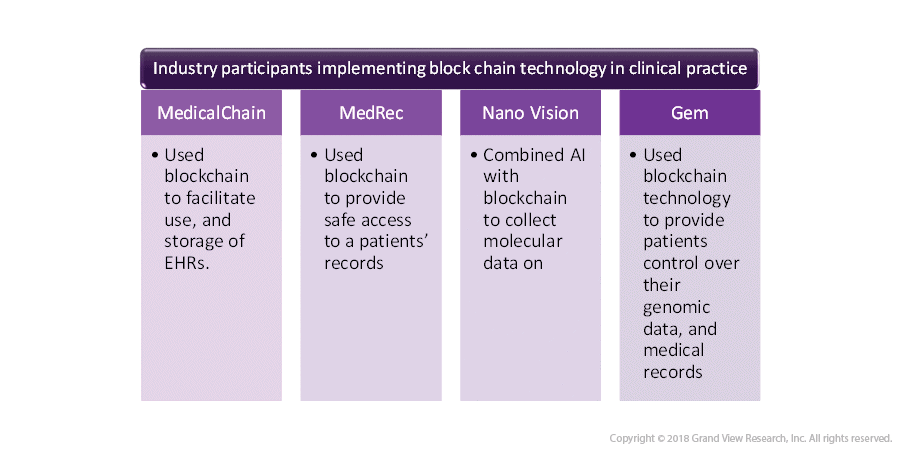
Owing to its benefits, blockchain software providers have entered the healthcare field as well. The year 2018 witnessed the execution of blockchain technology in pharmaceutical companies, hospitals and, other healthcare institutions. Following are some of the prominent industry participants that have developed blockchain solutions for operations in the healthcare sector.
11. Pharma 2018: Significant Investments And Technical Gains
The pharmaceutical market for 2018 was found to be remarkably stable albeit the swirling changes, and the biopharmaceutical market is growing rapidly enough to disregard. Contract manufacturing is anticipated to grow at a rate greater than 8% as indicated in the study on Biopharmaceutical CMO & CRO Market by Grand View Research Inc. This growth is expected to continue in the foreseeable future marked by the developments in single-use bioprocessing and continuous manufacturing. Into the bargain is the rapid expansion of manufacturing facilities as well as the R&D funding.
A) Go-Ahead Granted To Onpattro, RNAi Therapeutic
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals’ is at the zenith on receiving the approval after sixteen years of toiling for the development of a drug for the treatment of a rare genetic disorder called hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis.
- Just four years later to the discovery of RNA silencing characteristic of double-stranded RNA, this company entered the research zone.
After this success in 2018, the field associated with messenger RNA vaccines, antisense oligonucleotides, siRNA, or newer approaches seems to witness exponential growth, with a tangible excitement amongst the other participants in this domain. There are several companies that are waiting for the approvals, and many companies taking a small-molecule approach are also years away from the market, however, such companies have spellbound significant funding from VCs.
- The pharmaceutical industry is rapidly growing owing to the high market demand for new medications, therapy forms, an increase in digital medicine as well as changing regulations.
- For instance, according to the United Nations, the population in 2017 was estimated to be 7.6 billion and is expected to reach 9.8 billion by 2050 and 11.2 billion by 2100. Thus, the geriatric population will rise to 28% from 22% as of 2017.
- Additionally, the increasing urbanization and increasing middle class are making it more affordable for the individuals to have medications and drugs which has led to higher demand for medication.
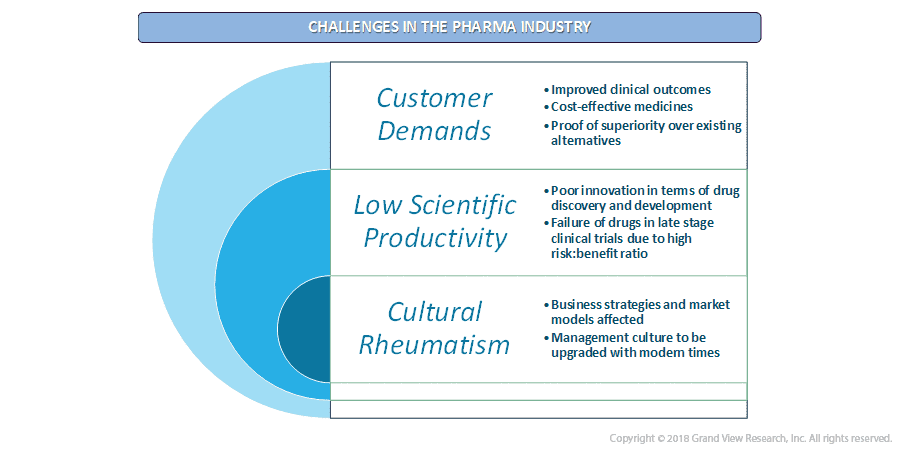
B) Public Relations In Pharma Industry: A Nightmare
- Issues pertaining to the rise in drug prices, public perception, the opioid crisis, and not to mention declining ROI in the sector are a few of the several challenges in this sector.
- The companies are continuously relying on licensing agreements and tangible acquisitions in order to refill the drug pipeline.
- In order to curb the ever-increasing drug development cost, these players are mining out various manufacturing strategies for effective operational management.
However, the market demand presents several growth opportunities for the well-orchestrated as well as the niche solution providers that are struggling to get on the top of the ladder with an upper hand on technology.









