Image by Jan Alexander from Pixabay
The last decade has witnessed some breakthroughs in the healthcare industry. With more access to information and unprecedented healthcare technology advancements, medical innovations have reached greater heights. In this blog, we will review 10 healthcare technology advancements that have permanently changed the face of the medical industry.
By 2024, the global clinical research organization market is set to exceed $51 billion. And while many CROs are either getting acquired or shutting down due to lack of funds, the existing ones are gearing up to take a more personalized drug discovery approach.
1. Neurostimulation for just about everything
Neurostimulation is a method used to adjust and program-specific parts of the nervous system through invasive or non-invasive techniques. During the early 2000s, this technology was primarily used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. But the last decade has found a new way to use it.
In 2013, the FDA approved NeuroPace RNS System’s RNS® Neurostimulator for treatment-resistant epilepsy. To treat medication-resistant depression, they also approved Brainsway™ Deep TMS in the same year and the MagVita TMS Therapy™ system in 2015. Following that, the FDA approved a wireless spinal cord stimulator in 2015, which helped with chronic back pain management.
Sleep apnea patients also experienced neurostimulation benefits after the FDA approved Inspire® Upper Airway Stimulation, a device designed for patients who couldn’t benefit from CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure).
2. Artificial ovaries transplant
Women diagnosed with cancer often choose to remove their ovaries, freeze them, and wait for them to be transplanted again until after the chemotherapy to avoid infertility. But the procedure is deemed risky as the organs may contain cancerous cells, which can reintroduce cancer into the body.
In 2018, Danish scientists engineered artificial ovaries on a tissue containing only protein and collagen sans the cancerous cells. They’re optimistic that this method can allow women to get pregnant ‘naturally’ and avoid cancer risks.
While still in its nascent stage, scientists have already successfully performed the procedure on mice and are hoping to introduce it to humans in the coming years.
3. Regenerative medicine and therapies
Before 2010, regeneration was merely a fascinating subject for movies. But the last decade has seen some remarkable development in the field of regenerative medicine and therapies.
Simply put, regenerative therapies focus on the body’s ability to repair or regrow a tissue – a phenomenon that’s quite prevalent among animals like lizards and sharks.
In 2016, the FDA approved MACI (Matrix-Induced Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation) – a more advanced version of Carticel, which is now being used to regrow injured cartilages in the lab that can be implanted back into the body.
4. Personalized drugs and 3D printed drugs
One of the biggest challenges in the medical field is the uniform performance of every drug available to the world. The only remotely customizable aspect was that of having a pill.
In 2017, the advancements in stereolithography – the technology of 3D printing – enabled doctors to customize drug doses and create more recent forms of dosage. Owing to this, patients can now avail a combination of treatments instead of relying on a single solution.
Presently, 3D printed drugs have also found a place in oncology clinical trials to provide patients with more than one treatment option.
5. Biotechnology for audio and vision restoration therapy
The year 2019 proved to be extraordinary for the treatment of auditory and visual disorders. With the advances in biotech, it was possible to reduce the computing devices’ size and create miniatures that are just as powerful as the larger devices.
Frequency Therapeutics’ FX-322 rose as one of the most advanced hearing loss treatment drugs in 2019. By injecting this slow-released gel into the ear, you can encourage the mature stem cells to multiply into more cells.
On the other hand, the Orion system by Second Sight Medical has become a highly efficient cortical visual prosthesis system in the last decade. It captures images using a miniature video camera and delivers them to the brain via a series of electrical pulses.
6. Genomic editing
Genome engineering might have made a name for itself in the early 90s, but it has become vastly more sophisticated in the last decade than it was back then.
Today, with genomic editing, the healthcare industry can change how genes interact with each other and make specific alterations to any living creature’s DNA.
In fact, one of the leading genome-editing companies, Intellia, is developing a biological tool called the CRISPR/Cas9 system, which they believe can permanently edit disease-associated genes using only one type of treatment.
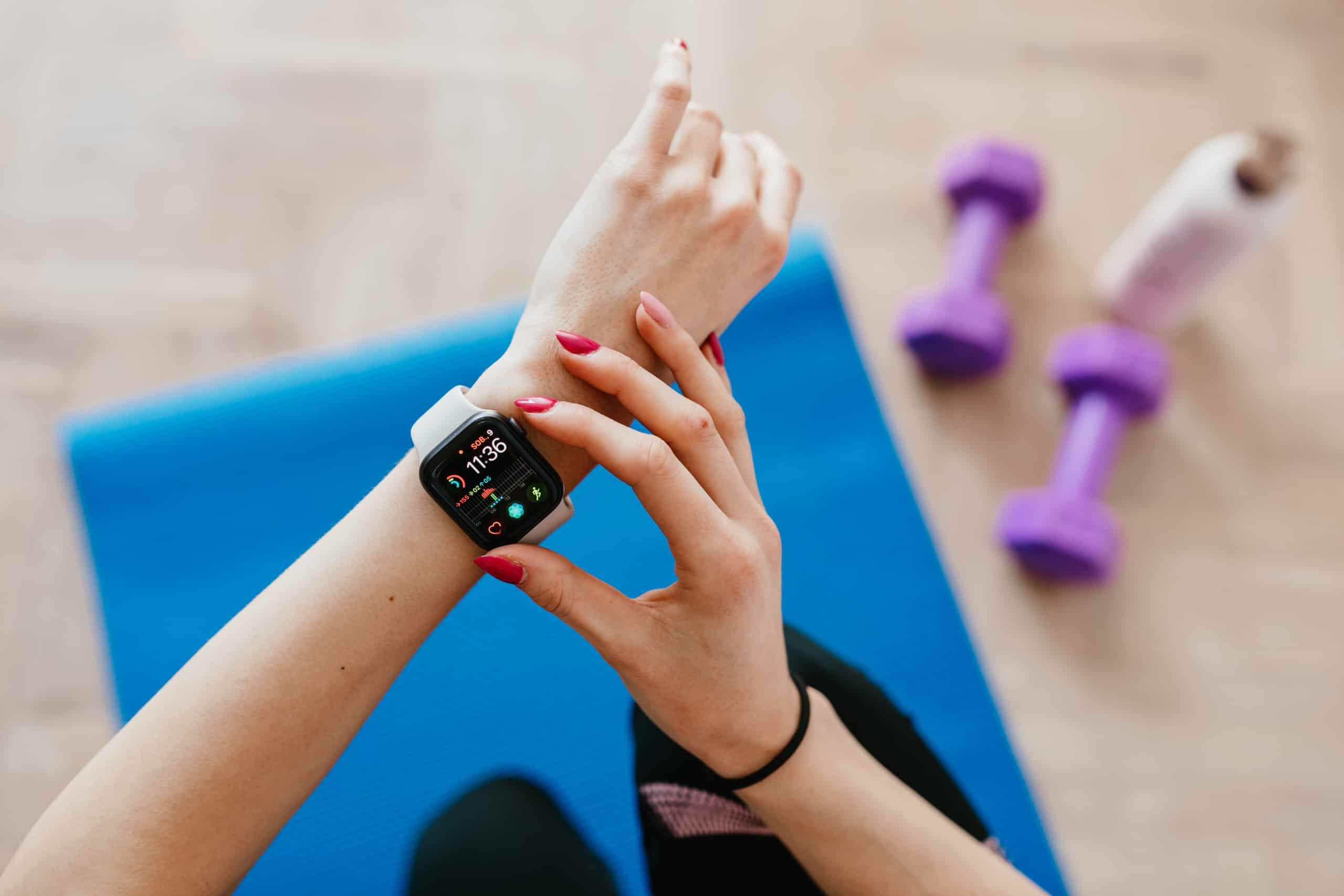

Photo by Karolina Grabowska from Pexels
7. Wearable medical devices
Following the emergence of iOS and Android’s health monitoring systems, medical technology has achieved new heights. In the last decade, patients have become more aware of their bodies as they grow closer to personal health trackers and sensors.
Currently, wearable technology is so ‘smart’ that it collects and stores data to assess the users’ health without the need for any paperwork.
Devices like the Apple Watches are also equipped to send alerts and notifications to healthcare providers in emergencies, thereby eliminating countless complications caused by a delay in accessing medical care.
8. Breakthrough in robotic surgery
In 2011, Argo’s ReWalk device made headlines after receiving FDA approval. The assistive exoskeleton-controlled system enabled patients with spinal cord injuries to stand, walk, and climb stairs.
Medtronic’s Hugo RAS system was another breakthrough that became the news of the year in 2019. The much-awaited robotic system was a more cost-effective solution than its competitors, along with previously offering a robot-assisted spinal surgical platform in the US.
Following suit, Medtech Zone recently launched a robotic surgery system called SSI MANTRA (Multi-Arm Novel Tele Robotic Assistance), which boasts surgical specialties in nearly all medicine branches.
9. A new drug with the potential to treat ALS
After gaining popularity on social media in 2014, the progressive neurodegenerative disease – Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) – made the news yet again in 2017 when Japan created a possible drug to prevent the condition.
The scientists developed a medicine called Radicava or Edaravone to prevent oxidative stress, which was reckoned to be the reason behind the nerve damage that later encouraged ALS progression.
10. Augmented and virtual realities for surgeries
A 2019 study revealed that surgeons trained using virtual reality systems had a 230% boost in their practical performance compared with that of the former surgeons.
On the other hand, augmented reality has become a driving force in healthcare in the last decade. While VR helps people improve their surgical performance, AR is allowing healthcare providers to better prepare for real-life operations.
By providing them with more accurate depictions of the body, the technology creates more polished and well-equipped healthcare professionals for the world.